Environmental Initiatives
The issue of global environmental problems, including global warming, is becoming increasingly serious with each passing year. The Kissei Group positions addressing these environmental challenges as a key management issue and believes that strengthening and promoting environmental management towards the realization of a decarbonized and circular society will contribute to the development of a sustainable society and lead to the sustainable growth of the company.
Based on this understanding, the group has decided to further strengthen its environmental initiatives across the board. In March 2025, the "Kissei Group Basic Environmental Policy" will be established, along with setting targets for reducing CO2 emissions.
Kissei Group Basic Environmental Policy (Established March 20, 2025)
1. Basic Philosophy
Under the group management philosophy of "Kissei will make contributions to society by creating harmony among the group’s working parts ," we will actively work to preserve the global environment as part of our corporate social responsibility, and contribute to the realization of an affluent and comfortable society.
2. Basic Policy
(1) We take global environmental issues seriously and promote the reduction of environmental impact throughout the value chain, recognizing that a series of corporate activities have various impacts on the environment.
(2) In order to work toward global environmental preservation, we will evaluate and analyze the impact of our business activities on the environment and nature, and set medium- and long-term goals to achieve net zero CO2 emissions by 2050, and strive for continuous improvement.
(3) Actively promote resource recycling, including energy and resource conservation, waste reduction, introduction of renewable energy, preservation of biodiversity, and appropriate use and discharge of water resources.
(4) Each and every employee will strictly adhere to all relevant environmental laws, regulations, agreements, and other requirements, and will actively promote activities to prevent environmental pollution by raising environmental awareness and improving ethical standards through environmental education.
Disclosure Based on the Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
The Kissei Group recognizes that global warming and the intensification of climate change are common challenges for humanity, threatening our lives, business continuity, and the sustainable development of society. We aim for environmental management integrated with our business activities by evaluating and analyzing the impact of climate change on our business operations, strengthening resilience against risks, and appropriately capturing opportunities presented by climate change to improve our business environment through decarbonization and energy-saving measures.
Kissei Pharmaceutical has identified "promotion of environmental management" as one of its materialities and has expressed support for the TCFD recommendations. Regarding risks and opportunities related to climate change, we analyze the medium- to long-term impact on our business activities within the framework of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures). Based on the impact on our business strategy, we prioritize and promote initiatives to address the intensification of weather-related disasters and to achieve carbon neutrality.
Understanding the TCFD
The TCFD was established in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) to investigate ways to disclose climate-related information and manage financial institutions. The TCFD recommends that companies disclose the risks and opportunities related to climate change according to the following four categories.

| Governance | Organizational governance in line with climate-related risks and opportunities |
| Strategy | Actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on business, strategy, and financial planning (if material information) |
| Risk Management | Climate-related risks identification, assessment, and management status |
| Metrics and Targets | Metrics and targets used to assess and manage climate-related risks and opportunities (if material information) |
Strategy
Regarding the impact of climate change on the Company’s business, The TCFD Project Team, a subordinate organization to the Sustainability Promotion Committee, led the creation of 1.5℃*1 and 4℃*2 climate change scenarios. They then identified risks and opportunities for each, focusing on the impact on business sites in the Pharmaceutical Business, the central business of the Group. These risks and opportunities were analyzed and assessed in terms of their financial impact and their likelihood of occurrence, then possible measures were considered and prioritized by the impact on our business strategy.
Under the 1.5℃ scenario, we face transition risks, such as higher costs stemming from enhanced policies and regulations related to decarbonization, and a fall in reputation in the eyes of stakeholders resulting from insufficient efforts to address climate change. The 4℃ scenario assumes that decarbonization is unsuccessful, leading to a 4℃ rise in the global average temperature. This introduces physical risks, which break down further into immediate risks, such as water damage caused by typhoons and heavy rain, and long-term risks caused by rising temperatures, such as higher air conditioning costs and higher costs for securing water resources.
On the other hand, we believe that climate change also brings opportunities. For example, it could lead to the introduction of highly-efficient equipment and a rise in corporate value, thanks to proactive efforts to combat climate change and proper disclosure of these efforts. Knowing this, we will continue to promote decarbonization and increasing our resilience in order to improve corporate value sustainably.
As a result of analysis and assessment, there were no risks identified that could have a significant impact on the business strategy.
*1 Created with reference to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA’s) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) and others.
*2 Created with reference to the International Energy Agency’s (IPCC’s) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) and others.
< Results of Scenario Analysis >
Transition Risks_1.5℃ Scenario
| Classification | High-Priority | Impact on the Company | Degree of Impact*1 | Countermeasures | Business Risks*2 |
| Transition Risks | Enhanced policies and regulations related to decarbonization | Addition of carbon pricing Company could incur an estimated cost of approximately ¥200 million due to carbon pricing (based on estimated CO2 emissions in fiscal 2030 of 9,979 tons at a rate of US$140 per ton*3) |
Medium | ・Reduce CO2 emissions by introducing renewable energy, upgrading to energy-saving equipment, and further promoting activities to save energy |
Low |
| Capital investment costs could increase as a result of new or enhanced decarbonization policies such as CO2 emission regulations | Low | • Systematically switch to energy-efficient equipment when upgrading and consider taking advantage of subsidies and other avenues |
Low | ||
| Requirement to implement climate change initiatives | Stakeholders’ evaluation of the Company could decline due to insufficient efforts to address climate change | High | • Gain stakeholder trust via sustainable efforts to address climate change-related issues and through appropriate disclosure |
Low |
*1 Degree of impact is based on the following criteria: high (over ¥500 million per year), medium (¥100-¥500 million per year), low (less than ¥100 million yen per year)
*2 Business risks are evaluated comprehensively, taking into consideration the degree of impact, frequency of occurrence, order of response, and other factors.
*3 Carbon prices in 2030 for advanced economies under the NZE scenario according to IEA World Energy Outlook 2021
Physical Risks_ 4℃ Scenario
| Classification | High-Priority | Impact on the Company | Degree of Impact*1 | Countermeasures | Business Risks*2 |
| Physical Risks (Immediate) | Intensification and increased frequency of natural disasters | Flooding could cause damage to key locations, leading to suspended operations and expenses to restore these operations, and could also affect the development pipeline and impact the steady supply of products | High | • Take appropriate measures to minimize damage to locations from floods and other disasters |
Low |
| Disasters could disrupt manufacturing due to damage incurred by suppliers, or hinder the steady supply of drugs by affecting the transportation network | High | • Maintain and improve the system for steady drug supply by keeping an inventory of drugs in conditions suited to their respective characteristics, and in decentralized locations • Reduce procurement risks by establishing multiple supply lines |
Low | ||
| Physical Risks (Long-Term) | Increased frequency of natural disasters could lead to higher insurance premiums | Low | • Make appropriate judgments that balance insurance premiums with actual risk, and take out policies that hedge risks |
Low | |
| Rising temperatures | Rising temperatures could lead to higher air-conditioning costs | Low | • Continue activities to instill the importance of saving energy among employees, and promote new activities • Introduce and shift to high-efficiency and energy-saving equipment |
Low | |
| Water shortages | A lack of water resources could lead to restrictions on water use, thereby disrupting operations, while costs related to securing water resources could increase | Low | • Increase information collection related to water withdrawal in surrounding areas and construct an emergency response system that factors in the risk of acquiring water resources*3 |
Low |
*1 Degree of impact is based on the following criteria: high (over ¥500 million per year), medium (¥100-¥500 million per year), low (less than ¥100 million yen per year)
*2 Business risks are evaluated comprehensively, taking into consideration the degree of impact, frequency of occurrence, order of response, and other factors.
*3 Water risks determined with reference to the AQUEDUCT Water Risk Atlas
Opportunity
| Classification | Item | Impact on the Company* | Degree of Impact |
| Opportunity | Resource efficiency | Costs for energy procurement and raw materials could be reduced by introducing new efficient technology and equipment | Low |
| Energy | The introduction of renewable energy could ensure stability of business versus future depletion of fossil fuels | Low | |
| Products and services | Demand could increase for existing pharmaceutical products in disease areas where morbidity increases as temperatures rise | Low | |
| Market | Demand and development opportunities could increase for treatment in disease areas where morbidity increases as temperatures rise | - | |
| Resilience | Climate change risk assessments and the continued implementation of climate change-related measures could minimize risks and enhance business stability | - | |
| Other | Active efforts to address climate change and conduct appropriate disclosure could build stakeholder trust (from customers, employees, investors, and students) and increase the Company’s reputation, thereby creating corporate value | - |
* Degree of impact is based on the following criteria: high (over ¥500 million per year), medium (¥100-¥500 million per year), low (less than ¥100 million yen per year)
Risk Management
Kissei has positioned risks related to climate change as important management risks, and the risks identified within the TCFD framework are reviewed at least once a year for their impact on business activities. Based on the level of impact, we consider cost-effectiveness and urgency, then prioritize, investigate, and implement response measures.
The Sustainability Promotion Committee will discuss and report on the management of these risks to the Board of Directors, the Audit & Supervisory Board, and the Risk Management Committee, an advisory body to the Board of Directors, to promote comprehensive Companywide risk management in an integrated manner.
Metrics and Targets
Towards achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, our group has set medium-term targets for CO2 emissions reduction and is actively promoting initiatives to meet these goals.
- • CO2 Emissions Target for Fiscal 2030 (Scope 1 + 2): 42% reduction compared to Fiscal 2020
- • CO2 Emissions Target for Fiscal 2050 (Scope 1 + 2): Net zero
Since fiscal 2022, our group has been progressively introducing electricity derived from renewable energy sources to reduce CO2 emissions (Scope 2). Moving forward, we will focus on reducing Scope 1 emissions. Additionally, we are currently working on calculating the total CO2 emissions (Scope 1 + 2) for the entire Kissei Group.
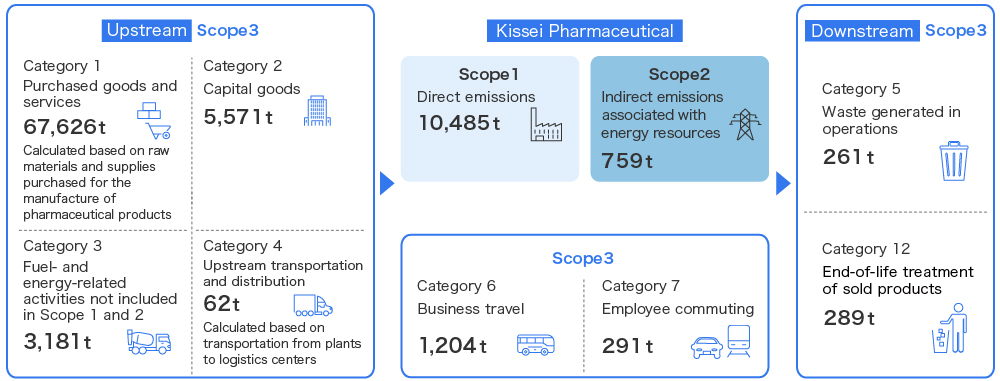
Scope 3 Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Supply Chain
We calculate Scope 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions based on the Basic Guidelines for Calculating Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Ver. 2.4), published by the Ministry of the Environment and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In fiscal 2023, Scope 3 emissions amounted to 78,485 tons, whereas total emissions (Scope 1, 2 and 3) amounted to 89,730 tons. Of these emissions, Scope 3 Category 1 emissions (CO2 emissions from purchased goods and services) accounted for 75.0% of total CO2 emissions.
Going forward, we aim to reduce CO2 emissions throughout our entire supply chain, and, in addition to efforts to reduce waste, we will also work to improve engagement with suppliers toward this goal.
Environmental Management System
Kissei promotes environmental management based on the ISO14001 standards for environmental management systems. Under the organizational structure of Kissei’s environmental management system, the vice-chair of the Sustainability Promotion Committee serves as the person in charge of environmental management.
Therefore, the vice-chair is in charge of the maintenance, management, and operation of environmental management throughout the Company. In addition, each business location has a person in charge of environmental management who is responsible for the maintenance, management, and operation of the environmental management system for their specific location.
ISO14001 Certification Status
| Kissei Pharmaceutical | Month of Acquisition |
| Head Office / Matsumoto Plants | September 2000 |
| Shiojiri Plants | September 2000 |
| Nutritional Business Center | September 2000 |
| Second Research Laboratories | September 2006 |
| Tokyo Head Office, Tokyo Head Office (Koishikawa) |
September 2006 |
| Central Research Laboratories | September 2007 |
| Group Company | Month of Acquisition |
| KISSEI COMTEC CO., LTD. | June 2002 |
|
HASHIBA TECHNOS CO., LTD. Head Office Facility Management Headquarters (shared with Kissei Pharmaceutical) |
February 2002 September 2000 |
Comprehensive Plan Related to Environmental Conservation
To realize our basic environmental policy, we set the reduction of environmental impacts in terms of energy use, CO2 emissions, and industrial waste generation as specific environmental metrics and targets, and we are working to achieve these targets by upgrading to energy-saving equipment, expanding the use of renewable energy, and promoting efforts to reduce, reuse, and recycle (3Rs).
Environmental Conservation Activity Achievements
The performance of Kissei Pharmaceutical's environmental conservation activities, including trends in energy usage, CO2 emissions, waste generation, and final waste disposal, is as follows.
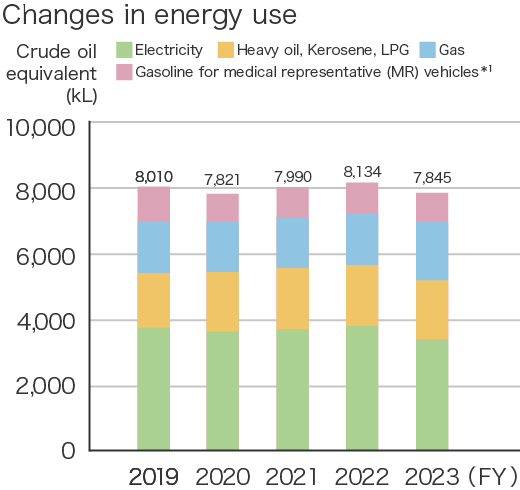
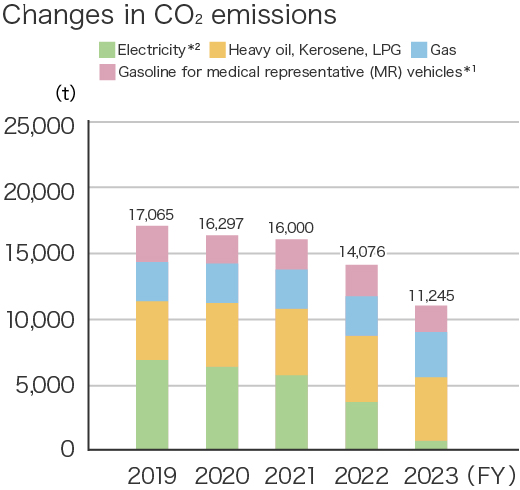
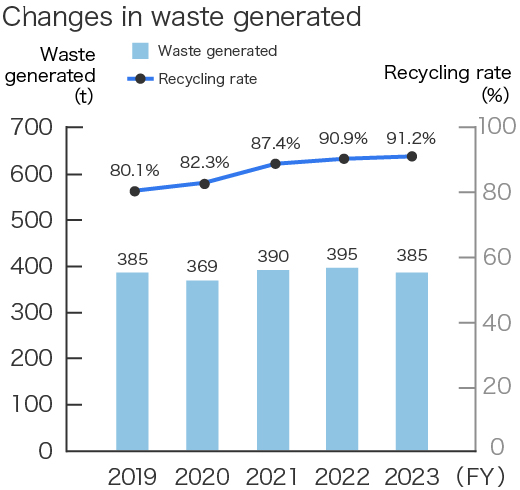
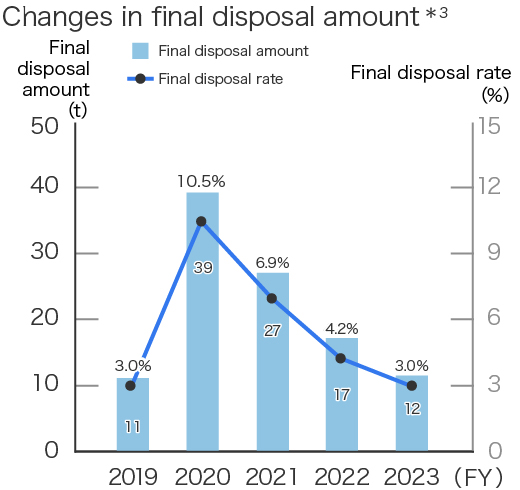
*1 From fiscal 2022, we changed the calculation method based on the composition ratio of gasoline and hybrid vehicles in MR vehicles. Therefore, the values of previous years have also been corrected retrospectively.
*2 The CO₂ emission factor of electricity was changed from the basic emission factor to the adjusted emission factor from fiscal 2022. Accordingly, the values of previous years have also been retrospectively revised.
*3 The volume of residue produced after intermediate treatment was reassessed following the adoption of the electronic manifest system in fiscal 2020.
The Environment and Kissei (Reducing Environmental Impact Companywide)
The figures below show the input of resources into Kissei Pharmaceutical for fiscal 2023, as well as the output in the form of emissions and waste generated in processes such as research, development, production, and sales. We are working to reduce our environmental impact based on this data.
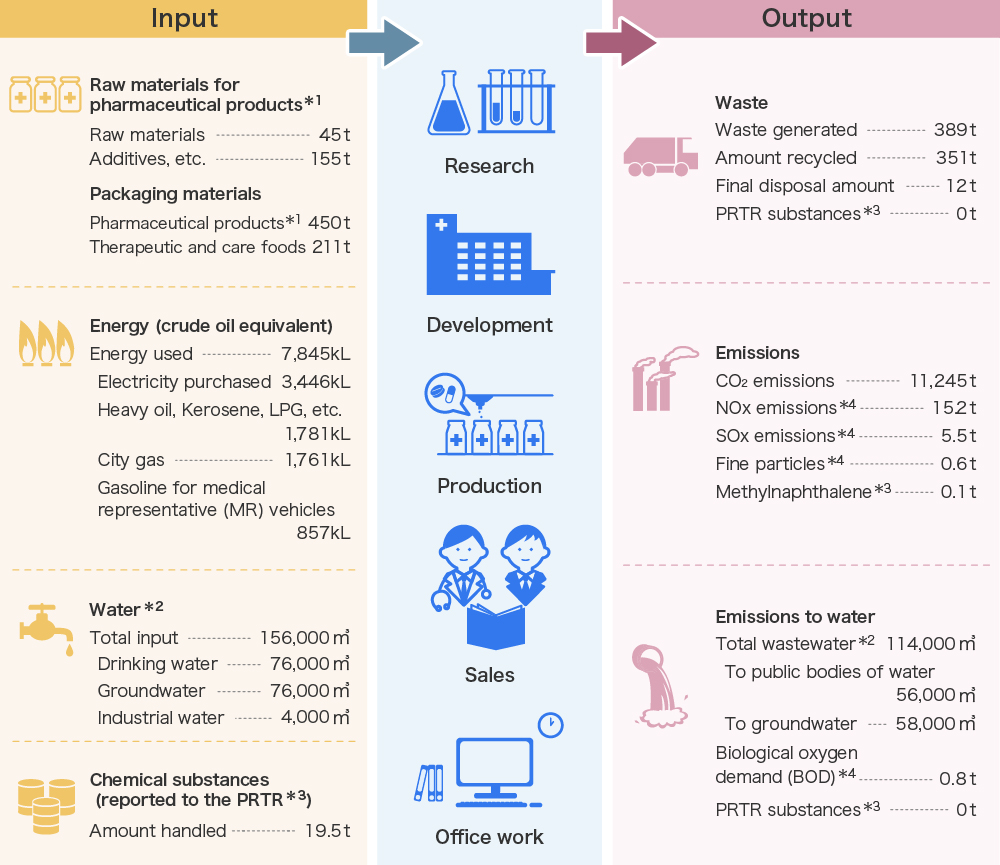
*1 The calculation method was revised following the launch of new products.
*2 Covering Head Office / Matsumoto Plants, Shiojiri Plants, Nutritional Business Center, Central Research Laboratories, Safety Research Laboratories, Joetsu Chemical Laboratories, Tokyo Head Office, Tokyo Head Office (Koishikawa)
*3 Data from business locations that handle one or more tons of applicable chemical substances annually
*4 Covering Head Office/Matsumoto Plants, Shiojiri Plants, Central Research Laboratories, Safety Research Laboratories, Joetsu Chemical Laboratories
Environmental Accounting
We have incorporated environmental accounting since fiscal 2004 to ascertain the cost of environmental conservation within business activities.
Going forward, we will continue to engage in effective environmental conservation activities.
- Target period:
- April 1, 2023, to March 31, 2024
- Scope of calculation:
- All business locations
- Calculation method:
- Based on “Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2005 edition,” Ministry of the Environment
- Investments and expenses:
- Investment amounts indicate the amount of investment in environmental-related facilities in a given fiscal year, and expenses indicate the amount of expenditures incurred for the purpose of environmental conservation and do not include depreciation expenses.
Environmental Conservation Costs
| Environmental Conservation Cost Categories | Investments* | Expenses | ||
| Costs within business area | ①Pollution prevention costs | Maintenance and management of air pollution prevention, water pollution prevention, etc. | 0 | 8,938 |
| ②Environmental conservation costs | Energy-saving measures, energy-saving equipment, etc. | 89,315 | 31,797 | |
| ③Resource recycling costs | Waste reduction, recycling, disposal and treatment costs, etc. | 0 | 34,914 | |
| Up/downstream costs | Container and packaging recycling consignment fees, etc. | 0 | 13,306 | |
| Management activity costs | Maintain and manage ISO14001, etc. |
4,698 | 1,520 | |
| R&D costs | ー | 0 | 0 | |
| Social activity costs | Sponsorship fees, etc. for environmental conservation groups, etc. | 0 | 230 | |
| Environmental damage response costs | ー | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 94,013 | 90,705 | ||
* Total of 11 investments of ¥500,000 or more
Environmental Conservation Effects
| Fiscal 2022 | Fiscal 2023 | Change(%) | |||
| CO2 emissions*1*2 | 14,075 | Tons | 11,245 | Tons | -20.1% |
| Energy used (oil equivalent) | 8,134 | kL | 7,845 | kL | -3.6% |
| Water used*3 | 151 | Thousands of ㎥ | 156 | Thousands of ㎥ | 3.3% |
| Wastewater*3 | 119 | Thousands of ㎥ | 114 | Thousands of ㎥ | -4.2% |
| Waste generated | 395 | Tons | 385 | Tons | -2.5% |
| Recycled | 359 | Tons | 351 | Tons | -2.2% |
| Final disposal | 17 | Tons | 12 | Tons | -29.4% |
*1 From fiscal 2022, the CO2 emission factor for electricity has been changed from the base emission factor to an adjusted emission factor. Figures for previous fiscal years have been retroactively adjusted and recalculated to reflect this change.
*2 From fiscal 2022, we changed the calculation method based on the composition ratio of gasoline and hybrid vehicles in MR vehicles. Therefore, the values of previous years have also been corrected retrospectively.
*3 Covering Head Office/Matsumoto Plants, Shiojiri Plants, Nutritional Business Center, Central Research Laboratories, Safety Research Laboratories, Joetsu Chemical Laboratories, Tokyo Head Office, Tokyo Head Office (Koishikawa)